Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme required to bring the amino acid to the ribosomes. So that the ribosome can polymerize the amino acids, that’s literally what a ribosome is. What is the function of aminoacyl-trna synthetase? Aminoacyl-Trna synthetase is a protein/RNA machine that polymerizes amino acids into a protein and this enzyme is required for that so here’s the idea aminoacyl tRNA synthetase is required to attach the tRNA to an amino acid.
Generic reaction of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
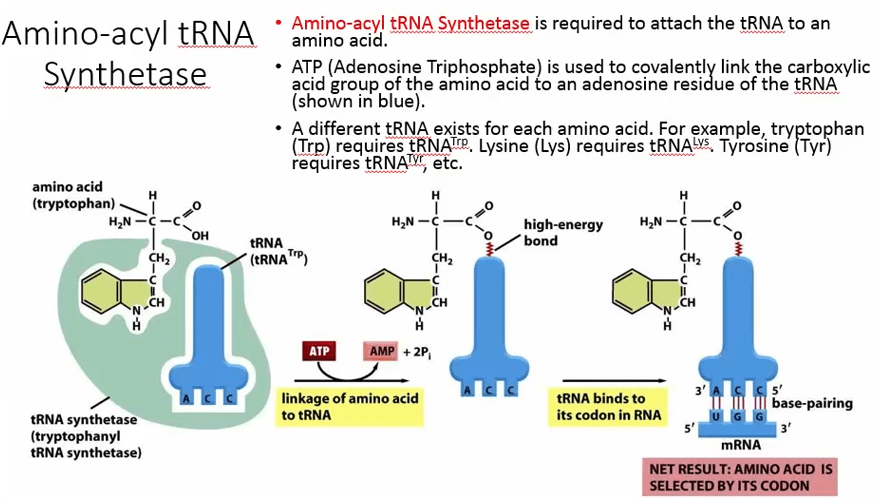
Brief Overview on “What is the function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase?”
Here’s the tRNA this is of course just a kind of rough sketch of it. this is a tRNA and then here’s a free amino acid. This particular one is tryptophan and what’s essentially going to happen in an ATP-dependent reaction.
Here’s the adenosine triphosphate in an atp-dependent reaction notice what happens is the amino acid essentially gets ligated to the tRNA so that you get this high-energy bond between the tRNA and the amino acid and what this essentially does is it activates the amino acid.
You have to imagine now that this amino acid which happens to be tryptophan is now covalently attached to this tRNA right here’s the tRNA and you know this reaction occurs in the cytosol but let’s say the ribosome here’s the ribosome way up here of course not drawn to scale.
well the job of the tRNA and remember T stands for what it stands for “transfer”. So literally what the tRNA is for is taking the amino acid and transferring it up here to the ribosome okay that’s why I called it a transfer RNA.
That’s literally what’s going to happen is it the transferring RNA is going to take the amino acid to the ribosome and facilitate the polymerization process which is carried out by the ribosome. so that’s what I want you to understand the actual transfer or the ligation of the amino acid to the tRNA is catalyzed by this enzyme aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
you need to be aware of this enzyme okay and what’s also important to understand is particular TRNAs are specific for particular amino acids so this is a good example if you’re using tryptophan you put tRNA and you put the three-letter abbreviation for tryptophan as a superscript. so if you have tRNA for tryptophan it’s tRNA superscript TRP.
Another example would be if you had a tRNA that’s specific for alanine you’d have tRNA and then in supers could you put ALA for alanine? if you had tRNA that was specific for phenylalanine you’d have tRNA and then put PAG up here for phenylalanine.
So particular TRNAs are specific for particular amino acids okay so there are lots of different tRNAs that you can have and the key is that they will particularly have different anticodons so this right here is the anticodon that binds to a particular codon in the mRNA that is complimentary.
One thing I do want you to be aware of is that this is an ATP-dependent reaction so anytime you need to polymerize amino acids into a protein it’s going to require a lot of energy because to activate the amino acid using aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for every ligation that you do if an amino acid to a tRNA you have to burn one ATP.
ATP is created mostly in the mitochondria through ATP synthase a process that we’ll talk about later in this blog in the last topic but ATP is like energy currency it’s like money from the sales perspective.
So if you want to do anything significant in terms of biosynthesis like biosynthesis of a protein you’ve got to waste some energy and usually the energy comes from things like ATP or gtp. that’s pretty typical so to make these proteins you’ve got to have a lot of energy available which means that you know for instance if you want to make proteins that’s a good indication that you’ve got to eat meals right you got to eat food with because that leads to the production of ATP.
if you’re anorexic or something like that you’re not getting lots of energy and so protein synthesis goes significantly now and that leads to the wasting away that people get when they’re anorexic okay so hopefully that makes a little sense you got to have ATP to catalyze the reaction of aminoacyl tRNA synthetase because this enzyme is required for protein synthesis.
Mutations in this enzyme are lethal the individual will probably not survive in utero they’ll die before they’re born so mutations in aminoacyl tRNA synthetase make protein synthesis almost impossible for levels to support life because keep in mind proteins in a lot of cases are enzymes and without enzymes remember that enzymatic processes uncapitalized are too slow to support life.
So this enzyme will never find any significant mutations in it. They’re lethal okay hopefully you understand that this enzyme is required to ligate the tRNA to the amino acid and then the transfer RNA takes the amino acid in the bound form to the ribosome.
When the amino acid is in the bound form to the tRNA you know you have all this business right here this is essentially this right here this is the adenosine moiety and then you have the rest of the tRNA down here this is the rest of the transfer RNA and then you have this amino acid here’s the carboxyl part of the amino acid and essentially it’s in an ester bond to the three prime hydroxyl group of the tRNA 3 prime end.
So right here this is this is the amino acid and that’s on the 3 prime end of the tRNA and the ribosome is going to use this to its advantage to polymerize the amino acids into proteins.
The ribosome is unique because we call it an enzyme but the catalytic component of this enzyme is ribosomal RNA. So this part right here is called peptidyl transferase this is the specific name of the actual enzymatic component of the ribosome but this is not the protein, it is ribosomal RNA.
This is an unusual enzyme because most enzymes are proteins and the main substrate of peptidyl transferase is the amino acid-like into the tRNA ok. So for the ribosome to be able to polymerize the amino acids into proteins okay you’ve got to have this aminoacyl tRNA synthetase that ligase the amino acid to the tRNA ok in general what the ribosome looks for is the tRNA.
The peptidyl transferase component is what works on this component if I was to shade this in this right here is literally the component that peptidyl transferase looks for ok it just deals with the amino acid component but the vast majority of the ribosome looks for this whole component right here.
This component is really what the ribosome essentially is looking for peptidyl transferase looks for the amino acid component but the whole thing is required you have to have the amino acid ligated to the tRNA and that process of synthesizing that is carried out by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.